What is the highest number of earthquakes on earth? Earthquakes: causes, consequences
Reports that a major earthquake has occurred in one area or another of the planet are not so rare in the modern press. Earthquakes are often accompanied by destruction of buildings, communications and industrial facilities, and sometimes by loss of life.
Unfortunately, science still cannot predict with sufficiently high reliability where the next vibration of the earth's solid earth will occur and how strong it will be, much less resist these vibrations.
What is an earthquake?
Vibrations of the earth's surface caused by tectonic processes, volcanic activity or rock falls are usually called earthquakes. Sometimes these vibrations can be artificial in nature and result from underground explosions or other industrial human activities. About a million earthquakes occur in the world every year, but the vast majority of them are not noticed by anyone except specialists armed with appropriate equipment - they are so insignificant.
Thus, earthquakes occurring on the ocean floor remain unnoticed: most vibrations are successfully damped by the water column. Only the strongest tremors, possessing enormous destructive power, generate giant waves that crash onto the nearby shore, causing enormous destruction and sometimes washing away entire cities. 
But, fortunately, this happens very rarely, and the majority of earthquakes are recorded only by special seismological equipment.
What causes earthquakes?
The most common cause of an earthquake is a tectonic shift deep in the earth's crust. The fact is that the surface of the Earth is not stationary; various processes constantly occur in it, especially noticeable in areas of so-called tectonic faults. In these places, rocks shift relative to each other, and the sliding of huge masses causes internal stress. When the energy of such stress accumulates, rock deformation occurs, which is accompanied either by the formation of a crack, or, conversely, by compression and swelling at the fracture site. The shock wave generated as a result of this process sometimes spreads over hundreds and even thousands of kilometers, causing vibrations of the earth's surface. Scientists distinguish seismic waves of two types: shear and compression.
Sometimes earthquakes are caused by other factors:
- volcanic activity: as a result of a volcanic eruption or lava outpouring, seismic waves are formed in the internal cavities of the earth’s crust, felt like tremors;
— landslide earthquakes: due to the collapse of a large mass of rock, a shock wave is formed, which is felt at some distance from the site of the collapse;
- artificial earthquakes are caused by human activity: strong underground explosions, for example, during mining or nuclear testing, the construction of dams and reservoirs that redistribute water pressure on rocks, etc.
What is the magnitude of an earthquake?
The strength of an earthquake is determined by its magnitude - a measure of the energy of the seismic waves that caused the tremors. 
The most common scale for measuring the magnitude of earthquakes is the Richter scale, but it only takes into account the strength of surface waves, and serious researchers use other scales for determining the strength of tremors - the magnitude of body waves and the magnitude of surface waves. These indicators are considered only together and allow the most objective assessment of each earthquake.
What should you do in case of an earthquake?
To avoid injury, let alone death, during an earthquake, it is recommended to take the following precautions.
1. At the first shock, you should leave the building as quickly as possible and, if possible, move some distance away from it. During the descent you cannot use the elevator!
2. When leaving the house, you need to turn off the gas and water supply, and turn off the electricity.
3. If you do not have time to leave the building, you should move away from the outer wall, choosing a place away from windows, mirrors and other glass objects, as well as hanging shelves and bulky furniture. It is best to hide under a sturdy table or bed. If the shocks are not too strong, it is safest to be in the doorway.
4. If you are driving in a car at the time of the earthquake, you need to stop and get out of the car, choosing a place as far as possible from houses, tall trees, bridges, viaducts, etc. 
5. In the coastal area, you should try to move as far from the coast as possible, for fear of a tsunami.
6. The subway is the safest place during an earthquake.
An earthquake is a natural phenomenon with destructive power; it is an unpredictable natural disaster that occurs suddenly and unexpectedly. An earthquake is an underground tremors caused by tectonic processes occurring inside the earth; these are vibrations of the earth's surface that arise as a result of sudden ruptures and displacements of sections of the earth's crust. Earthquakes occur anywhere on the globe, at any time of the year; it is virtually impossible to determine where and when, and what strength an earthquake will be.
They not only destroy our homes and change the natural landscape, but also raze cities and destroy entire civilizations; they bring fear, grief and death to people.

How is the strength of an earthquake measured?
The intensity of tremors is measured by points. Earthquakes with a magnitude of 1-2 are detected only by special devices - seismographs.
With an earthquake strength of 3-4 points, vibrations are already detected not only by seismographs, but also by people - objects around us sway, chandeliers, flower pots, dishes clink, cabinet doors open, trees and buildings sway, and the person himself sways.
At 5 points, it shakes even more strongly, wall clocks stop, cracks appear on buildings, and plaster crumbles.
At 6-7 points, the vibrations are strong, objects fall, paintings hanging on the walls, cracks appear on window glass and on the walls of stone houses.
Earthquakes of magnitude 8-9 lead to the collapse of walls and the destruction of buildings and bridges, even stone houses are destroyed, and cracks form on the surface of the earth.
A magnitude 10 earthquake is more destructive - buildings collapse, pipelines and railway tracks break, landslides and collapses occur.
But the most catastrophic in terms of the force of destruction are earthquakes of 11-12 points.
In a matter of seconds, the natural landscape changes, mountains are destroyed, cities turn into ruins, huge holes form in the ground, lakes disappear, and new islands may appear in the sea. But the most terrible and irreparable thing during such earthquakes is that people die. 
There is also another more accurate objective way of assessing the strength of an earthquake - by the magnitude of the vibrations caused by the earthquake. This quantity is called magnitude and determines the strength, that is, the energy of the earthquake, the highest value being magnitude-9.
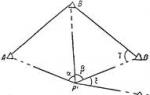
The source and epicenter of the earthquake
The force of destruction also depends on the depth of the earthquake source; the deeper the earthquake source occurs from the surface of the earth, the less destructive force the seismic waves carry.
The source occurs at the site of displacement of giant rock masses and can be located at any depth from eight to eight hundred kilometers. It doesn’t matter at all whether the displacement is large or not, vibrations of the earth’s surface still occur and how far these vibrations will spread depends on their energy and strength.
The greater depth of the earthquake source reduces destruction on the earth's surface. The destructiveness of an earthquake also depends on the size of the source. If the vibrations of the earth's crust are strong and sharp, then catastrophic destruction occurs on the surface of the Earth.
The epicenter of an earthquake should be considered the point above the source, located on the surface of the earth. Seismic or shock waves diverge from the source in all directions; the further away from the source, the less intense the earthquake. The speed of shock waves can reach eight kilometers per second.

Where do earthquakes most often occur?
Which corners of our planet are more earthquake-prone?
There are two zones where earthquakes occur most often. One belt begins at the Sunda Islands and ends at the Isthmus of Panama. This is the Mediterranean belt - it stretches from east to west, passes through mountains such as the Himalayas, Tibet, Altai, Pamir, Caucasus, Balkans, Apennines, Pyrenees and passes through the Atlantic.
The second belt is called the Pacific. This is Japan, the Philippines, and also covers the Hawaiian and Kuril Islands, Kamchatka, Alaska, and Iceland. It runs along the western coasts of North and South America, through the mountains of California, Peru, Chile, Tierra del Fuego and Antarctica.
There are also seismically active zones on the territory of our country. These are the North Caucasus, Altai and Sayan Mountains, the Kuril Islands and Kamchatka, Chukotka and the Koryak Highlands, Sakhalin, Primorye and the Amur Region, and the Baikal zone.
Earthquakes also often occur in our neighbors - in Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Armenia and other countries. And in other areas that are distinguished by seismic stability, tremors periodically occur.
The seismic instability of these belts is associated with tectonic processes in the earth's crust. Those territories where there are active smoking volcanoes, where there are mountain ranges and the formation of mountains continues, the foci of earthquakes are most often located there and tremors often occur in those places. 
Why do earthquakes happen?
Earthquakes are a consequence of tectonic movement occurring in the depths of our Earth, there are many reasons why these movements occur - these are the external influence of space, the Sun, solar flares and magnetic storms.
These are the so-called earth waves that periodically arise on the surface of our earth. These waves are clearly visible on the sea surface - sea ebbs and flows. They are not noticeable on the earth's surface, but are recorded by instruments. Ground waves cause deformation of the earth's surface.
Some scientists have suggested that the culprit of earthquakes may be the Moon, or rather, the vibrations occurring on the lunar surface also affect the earth's surface. It was observed that strong destructive earthquakes coincided with the full moon.
Scientists also note those natural phenomena that precede earthquakes - these are heavy, prolonged precipitation, large changes in atmospheric pressure, unusual air glow, restless behavior of animals, as well as an increase in gases - argon, radon and helium and uranium and fluorine compounds in groundwater .

Our planet continues its geological development, the growth and formation of young mountain ranges occurs, in connection with human activity, new cities appear, forests are destroyed, swamps are drained, new reservoirs appear, and the changes that occur in the depths of our Earth and on its surface cause all sorts of natural disasters.
Human activities also have a negative impact on the mobility of the earth's crust. A person who imagines himself to be a tamer and creator of nature thoughtlessly interferes with the natural landscape - demolishes mountains, erects dams and hydroelectric power stations on rivers, builds new reservoirs and cities.
And the extraction of minerals - oil, gas, coal, building materials - crushed stone, sand - affects seismic activity. And in those areas where there is a high probability of earthquakes, seismic activity increases even more. With his ill-considered actions, people provoke landslides, landslides and earthquakes. Earthquakes that occur due to human activity are called man-made.
Another type of earthquake occurs with human participation. During underground nuclear explosions, when tectonic weapons are tested, or during the explosion of a large amount of explosives, vibrations of the earth's crust also occur. The intensity of such tremors is not very great, but they can provoke an earthquake. Such earthquakes are called artificial.
There are still some volcanic earthquakes and landslide. Volcanic earthquakes occur due to high tension in the depths of the volcano; the cause of these earthquakes is volcanic gas and lava. The duration of such earthquakes is from several weeks to several months, they are weak and do not pose a danger to people.
Landslide earthquakes are caused by large landslides and landslides.
On our Earth, earthquakes occur every day; about one hundred thousand earthquakes a year are recorded by instruments. This incomplete list of catastrophic earthquakes that occurred on our planet clearly shows the losses humanity suffers from earthquakes.
Catastrophic earthquakes that have occurred in recent years
1923 - Japan epicenter near Tokyo, about 150 thousand people died.
1948 - Turkmenistan, Ashgabat is completely destroyed, about one hundred thousand dead.
1970 in Peru, a landslide caused by an earthquake killed 66 thousand residents of the city of Yungay.
1976 - China, the city of Tianshan is destroyed, 250 thousand dead. 
1988 - Armenia, the city of Spitak was destroyed - 25 thousand people died.
1990 - Iran, Gilan province, 40 thousand dead.
1995 - Sakhalin Island, 2 thousand people died.
1999 - Türkiye, the cities of Istanbul and Izmir - 17 thousand dead.
1999 - Taiwan, 2.5 thousand people died.
2001 - India, Gujarat - 20 thousand dead.
2003 - Iran, the city of Bam is destroyed, about 30 thousand people died.
2004 - the island of Sumatra - the earthquake and tsunami caused by the earthquake killed 228 thousand people.
2005 - Pakistan, Kashmir region - 76 thousand people died.
2006 - Java island - 5700 people died.
2008 - China, Sichuan province, 87 thousand people died.
2010 - Haiti, -220 thousand people died.
2011 - Japan - an earthquake and tsunami killed more than 28 thousand people, explosions at the Fukushima nuclear plant led to an environmental disaster.
Powerful tremors destroy the infrastructure of cities, buildings, depriving us of housing, causing enormous damage to the residents of those countries where the disaster occurred, but the most terrible and irreparable thing is the death of millions of people. History preserves the memory of destroyed cities, disappeared civilizations, and no matter how terrible the force of the elements, a person, having survived the tragedy, restores his home, builds new cities, erects new gardens and revives the fields on which he grows his own food.
How to behave during an earthquake

At the first tremors of an earthquake, a person experiences fear and confusion, because everything around begins to move, chandeliers sway, dishes clink, cabinet doors open, and sometimes objects fall, the earth disappears from under one’s feet. Many panic and begin to rush around, while others, on the contrary, hesitate and freeze in place.
If you are on the 1-2 floors, the first thing you should do is try to leave the room as quickly as possible and move to a safe distance from buildings, try to find an open place, pay attention to power lines, you should not be under them in case of strong shocks Wires may break and you may receive an electric shock.
If you are above the 2nd floor or did not have time to jump outside, try to leave the corner rooms. It is better to hide under a table or under a bed, stand in the opening of internal doors, in the corner of the room, but away from cabinets and windows, since broken glass and objects in cabinets, as well as cabinets and refrigerators themselves, can hit you and injure you if they fall. 
If you still decide to leave the apartment, then be careful, do not enter the elevator; during strong earthquakes, the elevator may turn off or collapse; it is also not recommended to run to the stairs. Flights of stairs may be damaged due to an earthquake, and a crowd of people rushing to the stairs will increase the load on them and the stairs may collapse. Going out onto balconies is just as dangerous; they can also collapse. You should not jump out of windows.
If tremors find you outside, move to an open space, away from buildings, power lines, and trees.
If you are in a car, stop at the side of the road, away from lamps, trees, and billboards. Don't stop in tunnels, under wires and bridges.
If you live in a seismically active area and earthquakes periodically shake your homes, then you should prepare yourself and your family for the possibility of a stronger earthquake. Determine in advance the safest areas in your apartment, take measures to strengthen your home, teach your children how to behave if children are alone at home during earthquakes.
Earthquakes are underground tremors accompanied by vibrations of the earth's surface.
Causes and types
The location of earthquake foci practically coincides with the boundaries of lithospheric plates
Earthquakes are tectonic, volcanic and landslide.
Tectonic earthquakes arise due to sharp displacements of mountain plates or as a result of the displacement of an oceanic platform under the continent. After all, the surface of the earth consists of continental and oceanic platforms, which, in turn, consist of separate blocks. When blocks are placed on top of each other, they can rise up and mountains are formed, or they can fall down and depressions are formed, or one of the plates will go under the other. All these processes are accompanied by vibrations or shaking of the earth.
Volcanic earthquakes occur due to the fact that streams of hot lava and gases press from below onto the surface of the Earth and thus make you feel that the earth is disappearing from under your feet. Volcanic earthquakes are usually not very strong, but can last quite a long time, sometimes several weeks. Often such earthquakes warn of an imminent volcanic eruption, which is even more dangerous than the earthquake itself.
Sometimes voids form underground, for example, under the influence of groundwater or underground rivers that erode the ground. In these places, the earth cannot withstand its own gravity and collapses, causing a slight shaking. It is called landslide earthquake.

After strong earthquakes, the landscape of the area changes, new lakes and mountains may appear
The most destructive and terrible are tectonic earthquakes. The place where plates collide or a powerful explosion occurs due to the release of energy accumulated in the earth is called earthquake source, or hypocenter. When the explosion occurs, a shock wave with a speed of more than 5 km/s (depending on the power of the explosion) begins to spread in all directions, reaches the surface of the earth (this area on the surface is called the epicenter, and it is located directly above the hypocenter) and diverges to the sides along circles. The epicenter is where the worst destruction occurs, and on the outskirts of the area affected by the earthquake, people may not even feel anything.
Strength of earthquakes
Earthquakes are one of the most dangerous natural phenomena. They bring great destruction and disaster, destroying not only material values, but also all living things, including people. The strength of an earthquake on the surface of the earth is measured in points on a special 12-point scale.

Point scale for measuring earthquake strength:
- 1 point - Not felt. Marked only with special devices
- 2 point - Very weak, noted only by domestic animals and some people in the upper floors of buildings
- 3 points - Weak. Only felt inside some buildings, like the shock of driving a truck
- 4 points - Moderate. You can hear the creaking of floorboards and beams, the clinking of dishes, and the shaking of furniture. Inside the building, the shaking is felt by most people
- 5 points - Quite strong. Tremors are felt in the rooms as if heavy objects were falling. Window glass breaks, chandeliers and furniture sway
- 6 point - Strong. Heavy furniture sways, dishes break, books fall from shelves, only very dilapidated houses are destroyed
- 7 point - Very strong. Old houses are being destroyed. In strong buildings, cracks appear and plaster crumbles. The water in rivers and lakes becomes cloudy
- 8 point - Destructive. Trees sway violently and strong fences break. Many strong buildings are being destroyed. Cracks appear in the soil
- 9 points - Devastating. Strong buildings are destroyed. Significant cracks appear in the soil
- 10 points - Destructive. Even strong buildings and bridges are destroyed. Landslides and collapses, cracks and bends in the soil occur
- 11th point - Disaster. Almost all stone buildings, roads, dams, and bridges are destroyed. Cracks with shifts form on the surface of the earth
- 12th point - Severe disaster. All structures are destroyed, the entire area is devastated. River courses are changing
Seismology

The seismograph pen draws a curved line in the form of sharp zigzags when tremors begin
Science studies earthquakes seismology. In different countries of the world, scientists conduct observations of the behavior of the earth's crust. They are helped in this by special instruments - seismographs. They measure and automatically record the slightest tremors occurring anywhere in the world. When the earth's surface oscillates, the main part of the seismograph - the suspended load - due to inertia, begins to move relative to the base of the device, and the recorder records the seismic signal transmitted to the marker.
An important task of seismology is earthquake prediction. Unfortunately, modern science cannot yet accurately predict them. Seismologists can more or less reliably determine the area and strength of an earthquake, but its onset is very difficult to predict.
Can an earthquake shake the Earth?
In mid-May 1960, one of the most significant and destructive earthquakes occurred in Chile - the Great Chilean Earthquake. Despite the fact that the main vibrations of the earth occurred in the southwestern part of South America - the epicenter of the earthquake was located near the city of Valdivia - their “echoes” reached other territories of our planet: in particular, the Hawaiian Islands and Japan. The phenomenon in which an earthquake that occurs in one part of the earth causes other parts of the earth to pulsate and tremble, even those located thousands of kilometers from the epicenter, is called “swing” or “vibration” of the earth.
An earthquake is a physical vibration of the lithosphere - the solid shell of the earth's crust, which is in constant motion. Often such phenomena occur in mountainous areas. It is there that underground rocks continue to form, causing the Earth's crust to be especially mobile.
Causes of the disaster
The causes of earthquakes can be different. One of them is the displacement and collision of oceanic or continental plates. During such phenomena, the surface of the Earth vibrates noticeably and often leads to the destruction of buildings. Such earthquakes are called tectonic. They may form new depressions or mountains.
Volcanic earthquakes occur due to the constant pressure of hot lava and all kinds of gases on the earth's crust. Such earthquakes can last for weeks, but, as a rule, they do not cause massive destruction. In addition, such a phenomenon often serves as a prerequisite for a volcanic eruption, the consequences of which can be much more dangerous for people than the disaster itself.

There is another type of earthquake - landslide, which occurs for a completely different reason. Groundwater sometimes forms underground voids. Under the pressure of the earth's surface, huge sections of the Earth fall down with a roar, causing small vibrations that can be felt many kilometers from the epicenter.
Earthquake scores
To determine the strength of an earthquake, they generally resort to either a ten- or twelve-point scale. The 10-point Richter scale determines the amount of energy released. The 12-point Medvedev-Sponheuer-Karnik system describes the impact of vibrations on the Earth's surface.
The Richter scale and the 12-point scale are not comparable. For example: scientists detonate a bomb underground twice. One at a depth of 100 m, the other at a depth of 200 m. The energy expended is the same, which leads to the same Richter rating. But the consequence of the explosion - displacement of the crust - has varying degrees of severity and has different effects on the infrastructure.
Degree of destruction

What is an earthquake from the point of view of seismic instruments? A one-point phenomenon is determined only by the equipment. 2 points can be sensitive animals, and also, in rare cases, especially sensitive people located on the upper floors. A score of 3 feels like the vibration of a building caused by a passing truck. A magnitude 4 earthquake causes slight rattling of glass. With a score of five, the phenomenon is felt by everyone, and it does not matter where the person is, on the street or in a building. An earthquake of magnitude 6 is called strong. It terrifies many: people run out into the street, and mother-in-laws form on some walls of houses. A score of 7 leads to cracks in almost all houses. 8 points: architectural monuments, factory chimneys, towers are knocked over, and cracks appear in the soil. 9 points lead to severe damage to houses. Wooden buildings either topple over or sag heavily. Magnitude 10 earthquakes lead to cracks in the ground up to 1 meter thick. 11 points is a disaster. Stone houses and bridges are collapsing. Landslides occur. No building can withstand 12 points. With such a catastrophe, the topography of the Earth changes, the flow of rivers is diverted and waterfalls appear.
Japanese earthquake
A destructive earthquake occurred in the Pacific Ocean, 373 km from the capital of Japan, Tokyo. This happened on March 11, 2011 at 14:46 local time.

A magnitude 9 earthquake in Japan led to massive destruction. The tsunami that hit the country's east coast flooded large parts of the coastline, destroying houses, yachts and cars. The height of the waves reached 30-40 m. The immediate reaction of people prepared for such tests saved their lives. Only those who left home in time and found themselves in a safe place were able to avoid death.
Japan earthquake victims
Unfortunately, there were no casualties. The Great East Japan Earthquake, as the event became officially known, claimed 16,000 lives. 350,000 people in Japan were left homeless, leading to internal migration. Many settlements were wiped off the face of the Earth, and there was no electricity even in large cities.
The earthquake in Japan radically changed the habitual way of life of the population and greatly undermined the economy of the state. The authorities estimated the losses caused by this disaster at $300 billion.
What is an earthquake from the point of view of a Japanese resident? It is a natural disaster that keeps the country in constant turmoil. The looming threat forces scientists to invent more accurate instruments for detecting earthquakes and more durable materials for building buildings.
Affected Nepal
On April 25, 2015, at 12:35 p.m., an almost 8-magnitude earthquake that lasted 20 seconds occurred in central Nepal. The following happened at 13:00. Aftershocks lasted until May 12. The reason was a geological fault on the line where the Hindustan plate meets the Eurasian plate. As a result of these tremors, the capital of Nepal, Kathmandu, moved to the south by three meters.

Soon the whole earth learned about the destruction caused by the earthquake in Nepal. Cameras installed directly on the street recorded the moment of the tremors and their consequences.
26 districts of the country, as well as Bangladesh and India, felt what an earthquake was like. Authorities are still receiving reports of missing people and collapsed buildings. 8.5 thousand Nepalese lost their lives, 17.5 thousand were injured, and about 500 thousand were left homeless.
The earthquake in Nepal caused real panic among the population. And it is not surprising, because people lost their relatives and saw how quickly what was dear to their hearts collapsed. But problems, as we know, unite, as was proven by the people of Nepal, who worked side by side to restore the former appearance of city streets.

Recent earthquake
On June 8, 2015, an earthquake of magnitude 5.2 occurred in Kyrgyzstan. This is the last earthquake to exceed magnitude 5.
Speaking about a terrible natural disaster, one cannot fail to mention the earthquake on the island of Haiti, which occurred on January 12, 2010. A series of tremors ranging from magnitude 5 to 7 claimed 300,000 lives. The world will remember this and other similar tragedies for a long time.
In March, the shores of Panama experienced a magnitude 5.6 earthquake. In March 2014, Romania and southwestern Ukraine learned the hard way what an earthquake is. Fortunately, there were no casualties, but many experienced anxiety before the disaster. In recent years, earthquake scores have not crossed the brink of catastrophe.
Earthquake Frequency
So, the movement of the earth's crust has various natural causes. Earthquakes, according to seismologists, occur up to 500,000 annually in different parts of the Earth. Of these, approximately 100,000 are felt by people, and 1,000 cause serious damage: they destroy buildings, highways and railways, break power lines, and sometimes carry entire cities underground.
In this article we will look at causes of earthquakes. The very concept of an earthquake is known to all people, and even children, but what are the reasons that suddenly the ground under your feet begins to move and everything around collapses?
First of all, it must be said that earthquakes are conventionally divided into several types: tectonic, volcanic, landslide, artificial and man-made. We will briefly look at all of them right now. If you want to know, be sure to read to the end.
Tectonic causes of earthquakes
Most often, earthquakes occur due to the fact that they are in constant motion. The top layer of lithospheric plates is called tectonic plates. The platforms themselves move unevenly and constantly press on each other. However, they remain alone for a long time.
Gradually, the pressure increases, as a result of which the tectonic plate makes a sudden push. It is he who produces vibrations in the surrounding rock, which is why an earthquake occurs.
San Andreas Fault
Transform faults are huge cracks in the Earth where plates rub against each other. Many readers should be aware that the San Andreas Fault is one of the most famous and longest transform faults in the world. It is located in the state of California in the USA.
 Photo of the San Andreas fault
Photo of the San Andreas fault The platforms moving along it cause devastating earthquakes in the cities of San Francisco and Los Angeles. Interesting fact: in 2015, Hollywood released a movie called “San Andreas Fault.” He talks about the corresponding disaster.
Volcanic causes of earthquakes
One of the causes of earthquakes is volcanoes. Although they do not produce strong vibrations of the earth, they last quite a long time. The reasons for the tremors are related to the fact that deep in the depths of the volcano the tension formed by lava and volcanic gases increases. As a rule, volcanic earthquakes last for weeks or even months.
However, history knows cases of tragic earthquakes of this type. An example is the Krakatoa volcano, located in Indonesia, which erupted in 1883.
 Krakatoa still gets excited sometimes. Real photo.
Krakatoa still gets excited sometimes. Real photo. The force of its explosion was at least 10 thousand times greater than the force of . The mountain itself was almost completely destroyed, and the island split into three small parts. Two-thirds of the land disappeared under water, and the rising tsunami destroyed everyone who still had a chance to escape. More than 36,000 people died.
Landslide causes of earthquakes
Earthquakes caused by giant landslides are called landslides. They are local in nature, and their strength is usually small. But there are exceptions here too. For example, in Peru, in 1970, a landslide with a volume of 13 million cubic meters descended from Mount Huascaran at a speed of over 400 km/h. About 20,000 people died.
Technogenic causes of earthquakes
Earthquakes of this type are caused by human activity. For example, artificial reservoirs in places not intended for this by nature provoke pressure on the plates with their weight, which serves to increase the number and strength of earthquakes.
The same applies to the oil and gas industry, when large quantities of natural materials are extracted. In a word, man-made earthquakes occur when a person took something from nature from one place and transferred it to another without asking.
Artificial causes of earthquakes
From the name of this type of earthquake, it is easy to guess that the blame for it lies entirely with man.
For example, North Korea tested a nuclear bomb in 2006, which caused a small earthquake recorded in many countries. That is, any activity of the inhabitants of the earth, which is obviously guaranteed to entail an earthquake, is an artificial cause of this type of disaster.
Is it possible to predict earthquakes?
Indeed it is possible. For example, in 1975, Chinese scientists predicted an earthquake and saved many lives. But this cannot be done with a 100% guarantee, even today. An ultra-sensitive device that records an earthquake is called a seismograph. The vibrations of the earth are recorded on the rotating drum by a recorder.
 Seismograph
Seismograph Animals also feel anxious before earthquakes. Horses begin to rear up for no apparent reason, dogs bark strangely, and snakes crawl out of their holes to the surface.
Earthquake scale
Typically, the strength of earthquakes is measured using the Earthquake Scale. We will present all twelve points so that you have an idea of what it is.
- 1 point (invisible) - the earthquake is recorded exclusively by instruments;
- 2 points (very weak) - can only be noticed by domestic animals;
- 3 points (weak) - noticeable only in some buildings. Feels like driving over bumps in a car;
- 4 points (moderate) - noticed by many people, may cause movement of windows and doors;
- 5 points (quite strong) - glass rattles, hanging objects sway, old whitewash may crumble;
- 6 points (strong) - with this earthquake, slight damage to buildings and cracks in low-quality buildings are noted;
- 7 points (very strong) - at this stage the buildings suffer significant damage;
- 8 points (destructive) - destruction is observed in buildings, chimneys and cornices are falling, cracks of several centimeters can be seen on the mountain slopes;
- 9 points (devastating) - earthquakes cause collapses of some buildings, old walls collapse, and the speed of crack propagation reaches 2 centimeters per second;
- 10 points (destructive) - collapses in many buildings, in most - serious damage. The soil is riddled with cracks up to 1 meter wide, and there are landslides and landslides all around;
- 11 points (catastrophe) - large landslides in mountainous areas, numerous cracks and a picture of general destruction of most buildings;
- 12 points (severe catastrophe) - the relief is changing globally almost before our eyes. Huge collapses and total destruction of all buildings.
In principle, on a twelve-point earthquake scale, any catastrophe caused by tremors of the earth’s surface can be assessed.