Why did the largest state in the world collapse? Largest states in history
The history of mankind is a continuous struggle for territorial dominance. Great empires either appeared on the political map of the world or disappeared from it. Some of them were destined to leave an indelible mark behind them.
Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 – 330 BC)
Cyrus II is considered the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. with the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e.
While conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored captured Jerusalem, like many Phoenician cities, facilitating the return of Jews from Babylonian captivity.
The Persian Empire under Cyrus extended its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus, Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its heyday under Darius I, who switched from conquests to internal politics. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the captured states.
In 330 BC. e. The weakening Persian Empire fell under the onslaught of the troops of Alexander the Great.
Roman Empire (27 BC – 476)

Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Beginning with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had a direct impact on European civilization and also left a cultural mark on the countries of North Africa and the Middle East.
The uniqueness of Ancient Rome is that it was the only state whose possessions included the entire Mediterranean coast.
At the height of the Roman Empire, its territories extended from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet.
Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of government of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization is based on. It was in imperial Rome that Christianity accepted the status of a state religion and began its spread throughout the world.
Byzantine Empire (395 – 1453)

The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end of the European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium was a kind of connecting link between the civilizations of the East and West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor.
But if Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the rich material culture of Byzantium, then the Old Russian state turned out to be the successor to its spirituality. Constantinople fell, but the Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow.
Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was open for the Turks.
Arab Caliphate (632-1258)

As a result of Muslim conquests in the 7th–9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose in the entire Middle Eastern region, as well as in certain regions of Transcaucasia, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history as the “Golden Age of Islam”, as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture.
One of the caliphs of the Arab state, Umar I, purposefully secured the character of a militant church for the Caliphate, encouraging religious zeal in his subordinates and prohibiting them from owning land property in the conquered countries. Umar motivated this by the fact that “the interests of the landowner attract him more to peaceful activities than to war.”
In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks was disastrous for the Caliphate, but the defeat of the Islamic state was completed by the Mongols.
Caliph An-Nasir, wanting to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and unknowingly opened the way for the destruction of the Muslim East by a Mongol horde of thousands.
Mongol Empire (1206–1368)
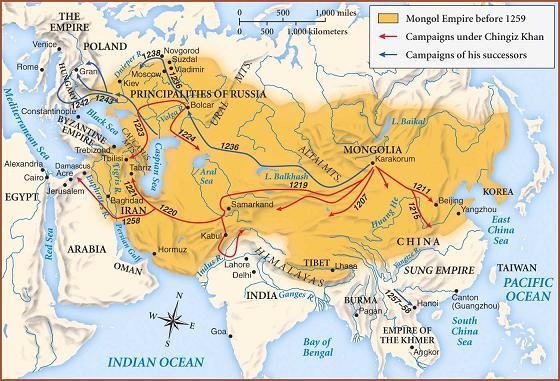
The Mongol Empire is the largest state formation in history by territory.
During the period of its power, towards the end of the 13th century, the empire extended from the Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of the Mongols' possessions reached 38 million square meters. km.
Given the enormous size of the empire, managing it from the capital, Karakorum, was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which became the Golden Horde.
The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence boiled down to the imposition of tribute on the conquered peoples. Everything collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisids, which not many armies could resist.
Inter-dynastic strife destroyed the empire - it was they who stopped the expansion of the Mongols to the West. This was soon followed by the loss of the conquered territories and the capture of Karakorum by Ming dynasty troops.
Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)

The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, as well as some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state.
For almost the entire period of the empire's existence, its structure had the character of a theocratic feudal state, in which the emperors claimed supreme power in the Christian world. However, the struggle with the papal throne and the desire to possess Italy significantly weakened the central power of the empire.
In the 17th century, Austria and Prussia moved to leading positions in the Holy Roman Empire. But very soon the antagonism of two influential members of the empire, which resulted in a policy of conquest, threatened the integrity of their common home. The end of the empire in 1806 was marked by the strengthening France led by Napoleon.
Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)

In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe.
The period of the greatest power of the Ottoman Empire occurred in the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved its greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
The borders of the empire of Suleiman I extended from Eritrea in the south to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the north, from Algeria in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east.
The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly revolved around Crimea and Transcaucasia. They were put to an end by the First World War, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the Entente countries, ceased to exist.
British Empire (1497–1949)

The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population.
The empire reached its greatest scale by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, including its colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which accounted for approximately 22% of the earth's land. The total population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British Crown.
The success of British colonial policy was facilitated by many factors: a strong army and navy, developed industry, and the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire significantly influenced global geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government throughout the world.
The decolonization of Britain occurred after the end of the Second World War. Although the country was among the victorious states, it found itself on the verge of bankruptcy. It was only thanks to an American loan of $3.5 billion that Great Britain was able to overcome the crisis, but at the same time lost world dominance and all its colonies.
Russian Empire (1721–1917)

The history of the Russian Empire dates back to October 22, 1721, after Peter I accepted the title of All-Russian Emperor. From that time until 1905, the monarch who became the head of the state was endowed with absolute power.
In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 square meters. km, and was the second (after British) in terms of population - about 178 million people.
Constant expansion of territory is a characteristic feature of the Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south Russia had to prove its territorial claims through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, and the British Empire.
The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The negative perception of Russia was facilitated by the appearance of the so-called “Testament of Peter the Great,” a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles. “The Russian state must establish power over all of Europe” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time.
Empire- when one person (monarch) has power over a vast territory inhabited by numerous peoples of different nationalities. This ranking is based on the influence, longevity and power of various empires. The list is based on the assumption that an empire should, most of the time, be ruled by an emperor or king, this excludes the modern so-called empires of the United States and the Soviet Union. Below is a ranking of the ten greatest empires in the world.
At the peak of its power (XVI–XVII), the Ottoman Empire was located on three continents at once, controlling most of Southeast Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. It consisted of 29 provinces and numerous vassal states, some of which were later absorbed into the empire. The Ottoman Empire was at the center of interaction between the eastern and western worlds for six centuries. In 1922, the Ottoman Empire ceased to exist.

The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of four Islamic caliphates (systems of government) created after the death of Muhammad. The empire, under the rule of the Umayyad dynasty, covered more than five million square kilometers, making it one of the largest in the world, as well as the largest Arab-Muslim empire ever created in history.
Persian Empire (Achaemenid)

The Persian Empire basically united all of Central Asia, which consisted of many different cultures, kingdoms, empires, and tribes. It was the largest empire in ancient history. At the peak of its power, the empire covered about 8 million square kilometers.

The Byzantine or Eastern Roman Empire was part of the Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. The permanent capital and civilizational center of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople. During its existence (more than a thousand years), the empire remained one of the most powerful economic, cultural and military forces in Europe despite setbacks and losses of territory, especially during the Roman-Persian and Byzantine-Arab wars. The Empire received its death blow in 1204 with the Fourth Crusade.

The Han Dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history in terms of scientific achievements, technological progress, economic, cultural and political stability. Even to this day, most Chinese call themselves Han people. Today, the Han Chinese are considered the largest ethnic group in the world. The dynasty ruled China for almost 400 years.

The British Empire covered more than 13 million square kilometers, roughly equivalent to about a quarter of our planet's land area. The empire's population was approximately 480 million people (approximately one-fourth of humanity). The British Empire is by far one of the most influential empires to ever exist in human history.

During the Middle Ages, the Holy Roman Empire was considered the "superpower" of its time. It consisted of eastern France, all of Germany, northern Italy and part of western Poland. It was officially dissolved on August 6, 1806, after which there appeared: Switzerland, Holland, the Austrian Empire, Belgium, the Prussian Empire, the principalities of Liechtenstein, the Confederation of the Rhine and the first French Empire.

The Russian Empire existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution in 1917. She was the heir to the kingdom of Russia, and the forerunner of the Soviet Union. The Russian Empire was the third largest state that ever existed, second only to the British and Mongol empires.

It all started when Temujin (later known as Genghis Khan, considered one of the most brutal rulers in history), vowed in his youth to bring the world to its knees. The Mongol Empire was the largest contiguous empire in human history. The capital of the state was the city of Karakorum. The Mongols were fearless and ruthless warriors, but they had little experience in ruling such a vast territory and the Mongol Empire quickly fell.

Ancient Rome made major contributions to the development of law, art, literature, architecture, technology, religion and language in the Western world. In fact, many historians consider the Roman Empire to be the "ideal empire" because it was powerful, fair, long-lasting, large, well-defended, and economically advanced. The calculation showed that from its foundation to its fall, a whopping 2214 years passed. From this it follows that the Roman Empire is the greatest empire of the ancient world.
Share on social media networks
Abstracts were prepared based on materials from the German magazine "Illustrierte Wissenschaft".
From the school history course we know about the emergence of the first states on earth with their unique way of life, culture and art. The distant and largely mysterious life of people of past times excited and awakened imagination. And, probably, for many it would be interesting to see maps of the greatest empires of antiquity, placed side by side. Such a comparison makes it possible to feel the size of the once gigantic state formations and the place they occupied on Earth and in the history of mankind.
Egypt. The empire reached its greatest size in 1450 BC. e.
Greece. The dark areas on the map indicate the lands where Greek culture flourished.
Persia. The territory of the empire in 500 BC. e.
India. The country's territory reached its largest size in 250 BC. e.
China occupied such territory in 221 BC. e.
The Roman Empire at its peak - the beginning of the 2nd century AD.
Byzantium in its heyday - VI century.
Arab Caliphate. It reached its greatest size in 632 AD. e. A118 years later, the area of the Caliphate was significantly reduced (dark shading).
The state is an ancient social entity and means a territory occupied by a settled population subject to the same authority. Ancient thinkers already thought about the essence of government. For example, the Greek philosopher Aristotle saw in the state the final natural form of community life, important for man, who by nature is a “political being.” Moreover, he considered the state “an environment for a completely happy life.”
In the Middle Ages and later, the concept of “state” began to include contractual principles between a person and the supreme power. In the state of nature, a person lacks not rights, the English thinkers of the 17th century John Milton and John Locke believed, but their security, which he finds in a state established by agreement precisely for this purpose.
A true son of the age of enlightenment, Jean-Jacques Rousseau saw the meaning of the formation of a state in respecting the interests of each of its citizens. People need it in order to “find a form of union that would protect and ensure the personality and property of each member of society so that each, connecting with others, would obey only himself and remain as free as before.” “Freedom is not alienable” is the main position of Rousseau.
Even 8-9 thousand years ago, people began to switch to a sedentary lifestyle. Agriculture and the first domestic animals appeared. The so-called Neolithic revolution took place, which brought people to new living conditions. Agriculture could already provide people with sufficient food, so hunting and gathering receded into the background. There was a division of labor between members of the same group, with leaders who governed communities of people. Over time, the need for public buildings arose, and the construction of palaces, temples, and fortresses began. Writing and the beginnings of arithmetic, astronomy and medicine appeared.
Rivers played a huge role in the formation of early civilizations. A river is not only a waterway, but also a stable harvest; it is no coincidence that it was in those distant times that people began to build canals and dams. But since the scattered tribes could not afford large reclamation buildings, groups of farmers united. The first state formations arose in Mesopotamia, between the Tigris and Euphrates, where a flourishing culture developed.
Modern archaeologists and historians identify several conditions that give the right to call ancient communities of people a state. The first of them is no less than five thousand people who worship the same gods. Power is equipped with an apparatus of officials, and writing is indispensable, existing in any form. Large buildings - palaces and temples - are also an obligatory attribute of statehood. The population is divided into specialties so that everyone can no longer do everything for themselves and their families. So, along with priests and soldiers, artists, philosophers, builders, blacksmiths, weavers, potters, reapers, merchants and so on appeared.
The ancient empires that played their role in human history had all of the above conditions. But in addition, they were characterized by long-term political stability and well-established communications to the most remote outskirts, without which it is impossible to manage vast territories. All great empires had large armies: the passion for conquest was almost manic. And the rulers of such states sometimes achieved impressive successes, subjugating vast lands on which giant empires arose. But time passed, and the giant left the historical stage.
First Empire
Egypt. 3000-30 BC
This empire lasted three millennia - longer than any other. The state arose, according to the latest data, more than 3000 years BC, and when the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt took place (2686-2181), the so-called Old Kingdom was formed. The entire life of the country was connected with the Nile River, with its fertile valley and delta near the Mediterranean Sea. Egypt was ruled by a pharaoh (the word means food warehouse), governors and officials were in place, and in general social life in the country was quite developed (see “Science and Life” No. 1, 1997 - “The Stone Age is not over yet” - and No. 5, 1997 - “Ancient Egypt. Pyramid of Power”). The elite of society included officers, scribes, land surveyors and local priests. The pharaoh was considered a living deity, and performed all the most important sacrifices himself.
The Egyptians fanatically believed in the afterlife; cultural objects and majestic buildings - pyramids and temples - were dedicated to it. The walls of the burial chambers, covered with hieroglyphs, told more about the life of the ancient state than other archaeological finds.
The history of Egypt falls into two periods. The first - from the foundation until 332 BC, when the country was conquered by Alexander the Great. And the second period is the reign of the Ptolemaic dynasty - the descendants of one of the generals Alexander the Great. In 30 BC, Egypt was conquered by a younger and more powerful empire - the Roman Empire.
Cradle of Western Culture
Greece. 700-146 BC
People settled the southern part of the Balkan Peninsula tens of thousands of years ago. But only from the 7th century BC can we talk about Greece as a large, culturally homogeneous entity, although with reservations: the country was a union of city-states that united during times of external threat, such as, for example, to repel Persian aggression.
Culture, religion and, above all, language were the framework within which the history of this country took place. In 510 BC, most cities were freed from the autocracy of the kings. Athens was soon ruled by democracy, but only male citizens had the right to vote.
The polity, culture and science of Greece became a model and an inexhaustible source of wisdom for almost all later European states. Already Greek scientists wondered about life and the Universe. It was in Greece that the foundations of such sciences as medicine, mathematics, astronomy and philosophy were laid. Greek culture ceased to develop when the Romans conquered the country. The decisive battle took place in 146 BC near the city of Corinth, when the troops of the Greek Achaean League were defeated.
The Dominion of the "King of Kings"
Persia. 600-331 BC
In the 7th century BC, the nomadic tribes of the Iranian Highlands rebelled against Assyrian rule. The winners founded the state of Media, which later, together with Babylonia and other neighboring countries, became a world power. By the end of the 6th century BC, it, led by Cyrus II and then his successors belonging to the Achaemenid dynasty, continued its conquests. In the west, the lands of the empire faced the Aegean Sea, in the east its border ran along the Indus River, in the south, in Africa, its possessions reached the first rapids of the Nile. (Most of Greece was occupied during the Greco-Persian War by the troops of the Persian king Xerxes in 480 BC.)
The monarch was called the "King of Kings", he stood at the head of the army and was the supreme judge. The domains were divided into 20 satrapies, where the king's viceroy ruled in his name. The subjects spoke four languages: Old Persian, Babylonian, Elamite and Aramaic.
In 331 BC, Alexander the Great defeated the hordes of Darius II, the last of the Achaemenid dynasty. Thus ended the history of this great empire.
Peace and love - for everyone
India. 322-185 BC
The legends dedicated to the history of India and its rulers are very fragmentary. Little information dates back to the time when the founder of the religious teaching, Buddha (566-486 BC), the first real person in the history of India, lived.
In the first half of the 1st millennium BC, many small states arose in the northeastern part of India. One of them - Magadha - rose to prominence thanks to successful wars of conquest. King Ashoka, who belonged to the Maurya dynasty, expanded his possessions so much that they occupied almost all of present-day India, Pakistan and part of Afghanistan. Administrative officials and a strong army obeyed the king. At first, Ashoka was known as a cruel commander, but, becoming a follower of the Buddha, he preached peace, love and tolerance and received the nickname “The Convert.” This king built hospitals, fought deforestation, and pursued a soft policy towards his people. His decrees that have reached us, carved on rocks and columns, are the oldest, accurately dated epigraphic monuments of India, telling about government, social relations, religion and culture.
Even before his rise, Ashoka divided the population into four castes. The first two were privileged - priests and warriors. The invasion of the Bactrian Greeks and internal strife in the country led to the collapse of the empire.
The beginning of more than two thousand years of history
China. 221-210 BC
During the period called Zhanyu in Chinese history, many years of struggle waged by many small kingdoms brought victory to the Qin kingdom. It united the conquered lands and in 221 BC formed the first Chinese empire led by Qin Shi Huang. The emperor carried out reforms that strengthened the young state. The country was divided into districts, military garrisons were established to maintain order and tranquility, a network of roads and canals was built, equal education was introduced for officials, and a single monetary system operated throughout the kingdom. The monarch established an order in which people were obliged to work where the interests and needs of the state required it. Even such a curious law was introduced: all carts must have an equal distance between the wheels so that they move along the same tracks. During the same reign, the Great Wall of China was created: it connected separate sections of defensive structures built earlier by the northern kingdoms.
In 210, Qing Shi Huang died. But subsequent dynasties left intact the foundations for building an empire laid by its founder. In any case, the last dynasty of Chinese emperors ceased to exist at the beginning of this century, and the borders of the state remain practically unchanged to this day.
An army that maintains order
Rome. 509 BC - 330 AD
In 509 BC, the Romans expelled the Etruscan king Tarquin the Proud from Rome. Rome became a republic. By 264 BC, her troops captured the entire Apennine Peninsula. After this, expansion began in all directions of the world, and by 117 AD the state stretched its borders from west to east - from the Atlantic Ocean to the Caspian Sea, and from south to north - from the rapids of the Nile and the coast of all of North Africa to the borders with Scotland and along the lower reaches of the Danube.
For 500 years, Rome was governed by two annually elected consuls and a senate, which was in charge of state property and finances, foreign policy, military affairs and religion.
In 30 BC, Rome became an empire led by Caesar, and essentially a monarch. The first Caesar was Augustus. A large and well-trained army participated in the construction of a huge network of roads, their total length being more than 80,000 kilometers. Excellent roads made the army very mobile and allowed it to quickly reach the most remote corners of the empire. The proconsuls appointed by Rome in the provinces - governors and officials loyal to Caesar - also helped keep the country from collapse. This was facilitated by the settlements of soldiers who had served in the conquered lands.
The Roman state, unlike many other giants of the past, fully corresponded to the concept of “empire”. It also became a model for future contenders for world domination. European countries inherited a lot from the culture of Rome, as well as the principles of building parliaments and political parties.
Uprisings of peasants, slaves and urban plebs, and the increasing pressure of Germanic and other barbarian tribes from the north forced Emperor Constantine I to move the capital of the state to the city of Byzantium, later called Constantinople. This happened in 330 AD. After Constantine, the Roman Empire was actually divided into two - Western and Eastern, ruled by two emperors.
Christianity is the stronghold of the empire
Byzantium. 330-1453 AD
Byzantium arose from the eastern remnants of the Roman Empire. The capital became Constantinople, founded by Emperor Constantine I in 324-330 on the site of the Byzantine colony (hence the name of the state). From that moment on, the isolation of Byzantium in the bowels of the Roman Empire began. The Christian religion played a major role in the life of this state, becoming the ideological foundation of the empire and the stronghold of Orthodoxy.
Byzantium existed for more than a thousand years. It reached its political and military power during the reign of Emperor Justinian I, in the 6th century AD. It was then that, having a strong army, Byzantium conquered the western and southern lands of the former Roman Empire. But within these limits the empire did not last long. In 1204, Constantinople fell to the attacks of the crusaders, which never rose again, and in 1453 the capital of Byzantium was captured by the Ottoman Turks.
In the name of Allah
Arab Caliphate. 600-1258 AD
The sermons of the Prophet Muhammad laid the foundation for the religious and political movement in Western Arabia. Called "Islam", it contributed to the creation of a centralized state in Arabia. However, soon as a result of successful conquests, a vast Muslim empire was born - the Caliphate. The presented map shows the greatest scope of the conquests of the Arabs, who fought under the green banner of Islam. In the East, the Caliphate included the western part of India. The Arab world has left indelible marks on human history, in literature, mathematics and astronomy.
From the beginning of the 9th century, the Caliphate gradually began to fall apart - the weakness of economic ties, the vastness of the territories subjugated by the Arabs, which had their own culture and traditions, did not contribute to unity. In 1258, the Mongols conquered Baghdad and the Caliphate broke up into several Arab states.
It is in history that answers to many modern questions can be found. Do you know about the largest empire that ever existed on the planet? TravelAsk will tell you about two world giants of the past.
Largest empire by area
The British Empire is the largest state that has ever existed in the history of mankind. Of course, here we are talking not only about the continent, but also about colonies on all inhabited continents. Just think: this was even less than a hundred years ago. At different times, the area of Britain was different, but the maximum was 42.75 million square meters. km (of which 8.1 million sq. km are territories in Antarctica). This is two and a half times larger than the current territory of Russia. This is 22% of land. The British Empire reached its peak in 1918.
The total population of Britain at its peak was about 480 million (about one-quarter of humanity). This is why English is so widespread. This is a direct legacy of the British Empire.
How the state was born
The British Empire grew over a long period: approximately 200 years. The 20th century marked the culmination of its growth: at this time the state possessed various territories on all continents. For this, it is called the empire “on which the sun never sets.”
And it all began in the 18th century quite peacefully: with trade and diplomacy, and occasionally with colonial conquests.

The Empire helped spread British technology, trade, the English language, and its form of government throughout the world. Of course, the basis of power was the navy, which was used everywhere. It ensured freedom of navigation and fought against slavery and piracy (slavery was abolished in Britain at the beginning of the 19th century). This made the world safer. It turns out that rather than seeking power over vast hinterlands for the sake of resources, the empire relied on trade and control over strategic points. It was this strategy that made the British Empire the most powerful.

The British Empire was very diverse, containing territories on every continent, creating a great variety of cultures. The state included a very diverse population, which gave it the ability to govern different regions either directly or through local rulers, an excellent skill for government. Just think: British power extended to India, Egypt, Canada, New Zealand and many other countries.

When the decolonization of the United Kingdom began, the British tried to introduce parliamentary democracy and the rule of law in the former colonies, but this was not successful everywhere. Great Britain's influence on its former territories is still noticeable today: most of the colonies decided that the Commonwealth of Nations replaced the Empire for them psychologically. Members of the Commonwealth are all former dominions and colonies of the state. Today it includes 17 countries, including the Bahamas and others. That is, they in fact recognize the monarch of Great Britain as their monarch, but locally his power is represented by the governor general. But it is worth saying that the title of monarch does not imply any political power over the Commonwealth Realms.
Mongol Empire
The second in area (but not in power) is the Mongol Empire. It was formed as a result of the conquests of Genghis Khan. Its area is 38 million square meters. km: this is slightly less than the area of Britain (and if you consider that Britain owned 8 million sq. km in Antarctica, the figure looks even more impressive). The territory of the state stretched from the Danube to the Sea of Japan and from Novgorod to Cambodia. This is the largest continental state in the history of mankind.

The state did not last long: from 1206 to 1368. But this empire influenced the modern world in many ways: it is believed that 8% of the planet’s population are descendants of Genghis Khan. And this is quite likely: Temujin’s eldest son alone had 40 sons.
At its height, the Mongol Empire included vast areas of Central Asia, Southern Siberia, Eastern Europe, the Middle East, China and Tibet. It was the world's largest land empire.
Its rise is astonishing: a group of Mongol tribes that numbered no more than a million people managed to conquer empires that were literally hundreds of times larger. How did they achieve this? Well-thought-out tactics of action, high mobility, the use of technical and other achievements of the captured peoples, as well as the correct organization of rear and supply.
.jpeg)
But here, of course, there could be no talk of any diplomacy. The Mongols completely slaughtered cities that did not want to obey them. More than one city was wiped off the face of the earth. Moreover, Temujin and his descendants destroyed great and ancient states: the state of the Khorezmshahs, the Chinese Empire, the Baghdad Caliphate, the Volga Bulgaria. Modern historians say that up to 50% of the total population died in the occupied territories. Thus, the population of the Chinese dynasties was 120 million people, after the Mongol invasion it decreased to 60 million.
Consequences of the Great Khan's invasions
By 1206, the commander Temujin united all the Mongol tribes and was proclaimed great khan over all tribes, receiving the title “Genghis Khan”. He captured northern China, devastated Central Asia, conquered all of Central Asia and Iran, ruining the entire region.

The descendants of Genghis Khan ruled an empire that captured most of Eurasia, including almost the entire Middle East, parts of Eastern Europe, China and Rus'. Despite all its power, the real threat to the dominance of the Mongol Empire was the enmity between its rulers. The empire split into four khanates. The largest fragments of Great Mongolia were the Yuan Empire, the Ulus of Jochi (Golden Horde), the state of the Hulaguids and the Chagatai Ulus. They, in turn, also failed or were conquered. In the last quarter of the 14th century, the Mongol Empire ceased to exist.
However, despite such a short reign, the Mongol Empire influenced the unification of many regions. For example, the eastern and western parts of Russia and the western regions of China remain united to this day, albeit under different forms of government. Rus' also gained strength: Moscow, during the Tatar-Mongol yoke, was granted the status of tax collector for the Mongols. That is, Russian residents collected tribute and taxes for the Mongols, while the Mongols themselves visited Russian lands extremely rarely. Eventually, the Russian people gained military power, allowing Ivan III to overthrow the Mongols under the Principality of Moscow.
At the height of the Roman Empire, its rule extended over vast territories - their total area was about 6.51 million square kilometers. However, in the list of the largest empires in history, the Roman Empire ranks only nineteenth.
What do you think, which one is the first?
The largest empire in the world in history
Mongolian
294 (21.8 % )
Russian
213 (15.8 % )
Spanish
48 (3.6 % )
British
562 (41.6 % )
Mongolian
118 (8.7 % )
Turkic Khaganate
18 (1.3 % )
Japanese
5 (0.4 % )
Arab Caliphate
18 (1.3 % )
Macedonian
74 (5.5 % )
Now we find out the correct answer...
Thousands of years of human existence have passed under the sign of wars and expansions. Great states arose, grew and collapsed, which changed (and some continue to change) the face of the modern world.
An empire is the most powerful type of state, where various countries and peoples are united under the rule of a single monarch (emperor). Let's look at the ten largest empires that have ever appeared on the world stage. Oddly enough, in our list you will not find either the Roman, or the Ottoman, or even the empire of Alexander the Great - history has seen more.
10. Arab Caliphate
Population: -
State area: - 6.7
Capital: 630-656 Medina / 656 - 661 Mecca / 661 - 754 Damascus / 754 - 762 Al-Kufa / 762 - 836 Baghdad / 836 - 892 Samarra / 892 - 1258 Baghdad
Beginning of rule: 632
Fall of an Empire: 1258
The existence of this empire marked the so-called. “The Golden Era of Islam” - the period from the 7th to the 13th centuries AD. e. The caliphate was founded immediately after the death of the creator of the Muslim faith, Muhammad in 632, and the Medina community founded by the prophet became its core. Centuries of Arab conquests increased the area of the empire to 13 million square meters. km, covering territories in all three parts of the Old World. By the middle of the 13th century, the Caliphate, torn apart by internal conflicts, was so weakened that it was easily captured first by the Mongols and then by the Ottomans, the founders of another great Central Asian empire.
9. Japanese Empire
Population: 97,770,000
State area: 7.4 million km2
Capital: Tokyo
Beginning of rule: 1868
Fall of the Empire: 1947
Japan is the only empire on the modern political map. Now this status is rather formal, but 70 years ago it was Tokyo that was the main center of imperialism in Asia. Japan, an ally of the Third Reich and fascist Italy, then tried to establish control over the western coast of the Pacific Ocean, sharing a vast front with the Americans. This time marked the peak of the territorial scope of the empire, which controlled almost the entire maritime space and 7.4 million square meters. km of land from Sakhalin to New Guinea.
8. Portuguese Empire
Population: 50 million (480 BC) / 35 million (330 BC)
State area: - 10.4 million km2
Capital: Coimbra, Lisbon
Since the 16th century, the Portuguese have been looking for ways to break Spanish isolation on the Iberian Peninsula. In 1497, they discovered a sea route to India, which marked the beginning of the expansion of the Portuguese colonial empire. Three years earlier, the Treaty of Tordesillas was concluded between the “sworn neighbors,” which actually divided the then-known world between the two countries, on unfavorable terms for the Portuguese. But this did not stop them from collecting more than 10 million square meters. km of land, most of which was occupied by Brazil. The handover of Macau to the Chinese in 1999 ended Portugal's colonial history.
7. Turkic Khaganate
Area - 13 million km2
one of the largest ancient states in Asia in the history of mankind, created by a tribal union of Turks (Turkuts) led by rulers from the Ashina clan. During the period of greatest expansion (end of the 6th century) it controlled the territories of China (Manchuria), Mongolia, Altai, East Turkestan, West Turkestan (Central Asia), Kazakhstan and the North Caucasus. In addition, the tributaries of the Kaganate were Sasanian Iran, the Chinese states of Northern Zhou, Northern Qi from 576, and from the same year the Turkic Kaganate seized the Northern Caucasus and Crimea from Byzantium.
6. French Empire
Population: -
State area: 13.5 million square meters. km
Capital: Paris
Beginning of rule: 1546
Fall of the Empire: 1940
France became the third European power (after Spain and Portugal) to become interested in the overseas territories. Since 1546, the time of the founding of New France (now Quebec, Canada), the formation of Francophonie in the world began. Having lost the American confrontation with the Anglo-Saxons, and also inspired by the conquests of Napoleon, the French occupied almost all of West Africa. In the middle of the twentieth century, the area of the empire reached 13.5 million square meters. km, more than 110 million people lived in it. By 1962, most of the French colonies had become independent states.
Chinese Empire
5. Chinese Empire (Qing Empire)
Population: 383,100,000 people
State area: 14.7 million km2
Capital: Mukden (1636–1644), Beijing (1644–1912)
Beginning of rule: 1616
Fall of the Empire: 1912
The most ancient empire of Asia, the cradle of oriental culture. The first Chinese dynasties ruled from the 2nd millennium BC. e., but a unified empire was created only in 221 BC. e. During the reign of the Qing, the last monarchical dynasty of the Celestial Empire, the empire occupied a record area of 14.7 million square meters. km. This is 1.5 times more than the modern Chinese state, mainly due to Mongolia, now independent. In 1911, the Xinhai Revolution broke out, putting an end to the monarchical system in China, turning the empire into a republic.
4. Spanish Empire
Population: 60 million
State area: 20,000,000 km2
Capital: Toledo (1492-1561) / Madrid (1561-1601) / Valladolid (1601-1606) / Madrid (1606-1898)
Fall of the Empire: 1898
The period of world domination of Spain began with the voyages of Columbus, which opened new horizons for Catholic missionary work and territorial expansion. In the 16th century, almost the entire Western Hemisphere was “at the feet” of the Spanish king with his “invincible armada.” It was at this time that Spain was called “the country where the sun never sets,” because its possessions covered a seventh of the land (about 20 million sq. km) and almost half of the sea routes in all corners of the planet. The greatest empires of the Incas and Aztecs fell to the conquistadors, and in their place a predominantly Spanish-speaking Latin America emerged.
3. Russian Empire
Population: 60 million
Population: 181.5 million (1916)
State area: 23,700,000 km2
Capital: St. Petersburg, Moscow
Fall of the Empire: 1917
The largest continental monarchy in human history. Its roots reach back to the times of the Moscow principality, then the kingdom. In 1721, Peter I proclaimed the imperial status of Russia, which owned vast territories from Finland to Chukotka. At the end of the 19th century, the state reached its geographical apogee: 24.5 million square meters. km, about 130 million inhabitants, over 100 ethnic groups and nationalities. Russian possessions at one time included the lands of Alaska (before its sale by the Americans in 1867), as well as part of California.
2. Mongol Empire
Population: more than 110,000,000 people (1279)
State area: 38,000,000 sq. km. (1279)
Capital: Karakorum, Khanbalik
Beginning of rule: 1206
Fall of the Empire: 1368
The greatest empire of all times and peoples, whose raison d'etre was one - war. The Great Mongolian State was formed in 1206 under the leadership of Genghis Khan, expanding over several decades to 38 million square meters. km, from the Baltic Sea to Vietnam, killing every tenth inhabitant of the Earth. By the end of the 13th century, its Uluses covered a quarter of the land and a third of the planet's population, which then numbered almost half a billion people. The ethnopolitical framework of modern Eurasia was formed on the fragments of the empire.
1. British Empire
Population: 458,000,000 people (approximately 24% of the world's population in 1922)
State area: 42.75 km2 (1922)
Capital London
Beginning of rule: 1497
Fall of the Empire: 1949 (1997)
The British Empire is the largest state that has ever existed in the history of mankind, with colonies on all inhabited continents.
Over the 400 years of its formation, it withstood competition for world domination with other “colonial titans”: France, Holland, Spain, Portugal. During its heyday, London controlled a quarter of the world's landmass (over 34 million sq. km) on all inhabited continents, as well as vast expanses of ocean. Formally, it still exists in the form of the Commonwealth, and countries such as Canada and Australia actually remain subject to the British crown.
The international status of the English language is the main legacy of Pax Britannica.
Something else interesting for you from history: remember, or for example. Here you go. maybe you didn't know that there was
The original article is on the website InfoGlaz.rf Link to the article from which this copy was made -




